Is salicylic acid polar or nonpolar – Salicylic acid, a ubiquitous molecule with a broad spectrum of applications, raises a fundamental question: is it polar or nonpolar? This inquiry delves into the molecular structure, functional groups, and polarity of salicylic acid, unveiling its profound implications in various industries.
The polarity of salicylic acid, stemming from its unique molecular architecture, influences its interactions with solvents, dictates its solubility, and governs its behavior in biological systems. By elucidating the polar nature of salicylic acid, we gain insights into its diverse applications, ranging from pharmaceuticals to skincare.
Chemical Properties of Salicylic Acid
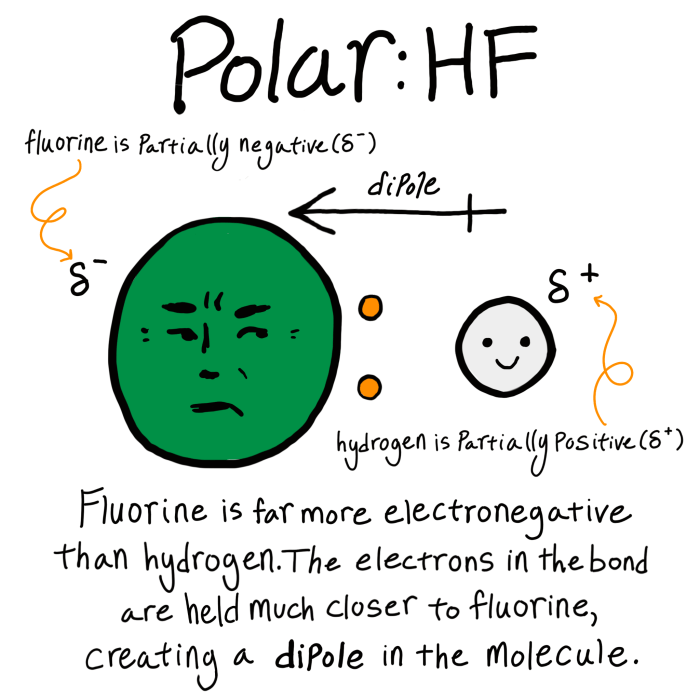
Salicylic acid, a widely recognized organic compound, possesses a distinctive molecular structure that governs its chemical properties and diverse applications. Its molecular formula, C7H6O3, reveals a benzene ring adorned with a carboxyl group (-COOH) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) as functional groups.
Functional Groups and Polarity, Is salicylic acid polar or nonpolar
The presence of these functional groups significantly influences the polarity of salicylic acid. The carboxyl group, with its polar C=O and O-H bonds, contributes a partial negative charge to the molecule. Conversely, the hydroxyl group, with its polar O-H bond, introduces a partial positive charge.
These opposing charges create a dipole moment, rendering salicylic acid a polar molecule.
The polarity of salicylic acid affects its solubility, reactivity, and interactions with other molecules. Its polar nature allows it to form hydrogen bonds with water and other polar solvents, enhancing its solubility in aqueous environments.
Polarity of Salicylic Acid
In the realm of organic chemistry, polarity plays a crucial role in determining the physical and chemical properties of molecules. Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrical charge within a molecule, resulting in a separation of positive and negative charges.
The molecular structure of salicylic acid dictates its polarity. The molecule comprises a benzene ring substituted with a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH). The electronegative oxygen atoms in both functional groups attract electrons towards themselves, creating a partial negative charge.
Conversely, the hydrogen atoms in these groups exhibit a partial positive charge.
Polar and Nonpolar Solvents
Polar solvents, such as water and methanol, possess a permanent dipole moment due to the uneven distribution of charge. They are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with polar molecules like salicylic acid. Nonpolar solvents, such as hexane and toluene, lack a permanent dipole moment and do not participate in hydrogen bonding.
Salicylic acid exhibits greater solubility in polar solvents compared to nonpolar solvents. This is attributed to the ability of polar solvents to form hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl and carboxylic acid groups of salicylic acid, leading to stronger intermolecular interactions.
Applications of Salicylic Acid: Is Salicylic Acid Polar Or Nonpolar
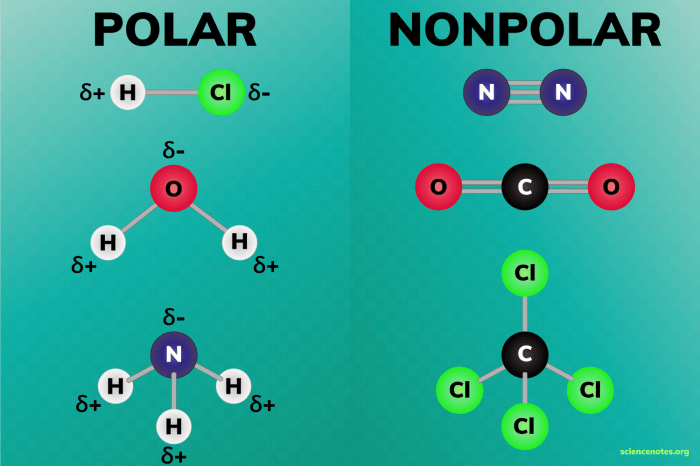
Salicylic acid, with its unique polarity, finds applications in various industries due to its antiseptic, keratolytic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
The polarity of salicylic acid allows it to dissolve in both water and oil, making it an effective ingredient in both water-based and oil-based products.
Pharmaceuticals
Salicylic acid is widely used in pharmaceuticals due to its anti-inflammatory and keratolytic properties. It is a common ingredient in acne treatments, as it helps reduce inflammation and unclog pores.
Cosmetics
In the cosmetics industry, salicylic acid is used as an exfoliating agent. It helps remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, resulting in smoother and brighter skin.
Agriculture
Salicylic acid is also used in agriculture as a plant growth regulator. It helps promote root development and can be used to control fruit ripening.
Comparison with Other Molecules
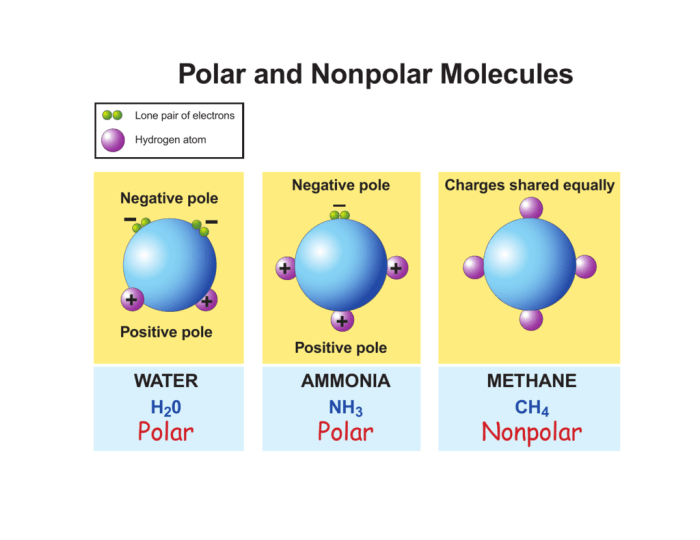
Salicylic acid exhibits polarity that differs from other similar molecules due to variations in their molecular structures and functional groups. These differences impact the polarity of the molecules and influence their behavior in various applications.
Factors contributing to polarity differences include the presence of electronegative atoms, the distribution of electron density, and the molecular geometry. The polarity of a molecule is determined by the vector sum of the bond polarities within the molecule.
Polarity of Salicylic Acid and Other Molecules
| Molecule | Polarity |
|---|---|
| Salicylic acid | Polar |
| Benzoic acid | Less polar than salicylic acid |
| Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) | Less polar than salicylic acid |
| Phenol | More polar than salicylic acid |
Detailed FAQs
What is the molecular structure of salicylic acid?
Salicylic acid possesses a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) attached.
How does the polarity of salicylic acid influence its solubility?
Salicylic acid is more soluble in polar solvents, such as water and ethanol, due to its polar nature.
What are some applications of salicylic acid?
Salicylic acid finds applications in pharmaceuticals (as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent), skincare (as an exfoliant), and agriculture (as a plant growth regulator).