Ap biology 042 biological molecules – Embark on a scientific odyssey with AP Biology 042: Biological Molecules. This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricate world of the building blocks of life, revealing their structures, functions, and significance in biological processes. Prepare to be captivated as we unravel the secrets of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, unlocking the mysteries of life itself.
Biological Molecules: Ap Biology 042 Biological Molecules
Biological molecules are the fundamental building blocks of life, providing structure, function, and energy for all living organisms. They are classified into four main groups: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each group has a unique molecular structure and set of functions, contributing to the complexity and diversity of life.
Carbohydrates
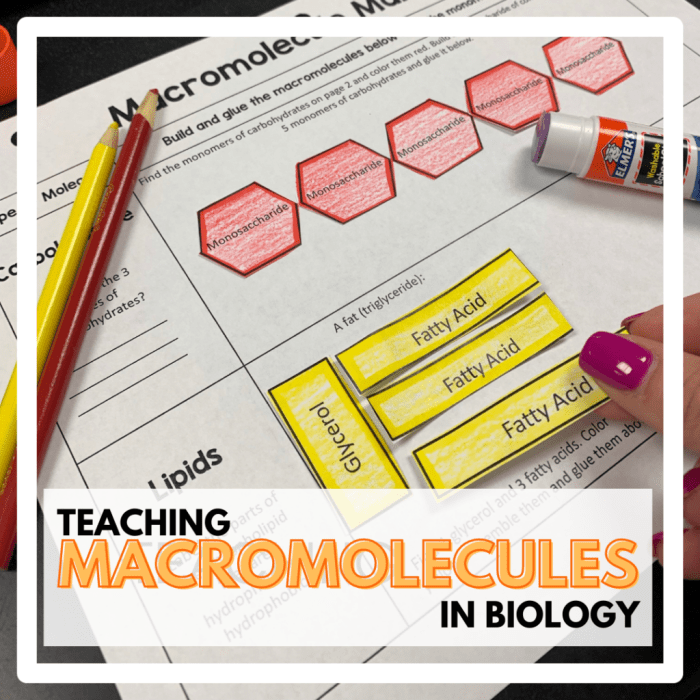
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and they are the primary source of energy for living organisms. They are classified into three main groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, while disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides linked together, such as sucrose and lactose.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of many monosaccharides linked together, such as starch and cellulose. Carbohydrates provide energy through the process of cellular respiration, where they are broken down into glucose and used as fuel for cellular processes. They also play a structural role in cell walls and other cellular components.
Proteins
Proteins are composed of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. They are essential for a wide range of biological functions, including enzyme catalysis, hormone regulation, structural support, and immune defense. Proteins have four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
The primary structure refers to the sequence of amino acids, while the secondary structure refers to the folding of the protein into alpha helices or beta sheets. The tertiary structure refers to the further folding of the protein into a three-dimensional shape, and the quaternary structure refers to the interactions between multiple protein subunits.
The structure of a protein determines its function, and changes in structure can lead to changes in function.
Lipids
Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and they are often hydrophobic. They include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids serve as energy storage molecules, providing a concentrated source of energy for cells.
They also form the structural components of cell membranes, providing a barrier between the cell and its surroundings. Additionally, lipids act as signaling molecules, regulating various cellular processes.
Nucleic Acids, Ap biology 042 biological molecules
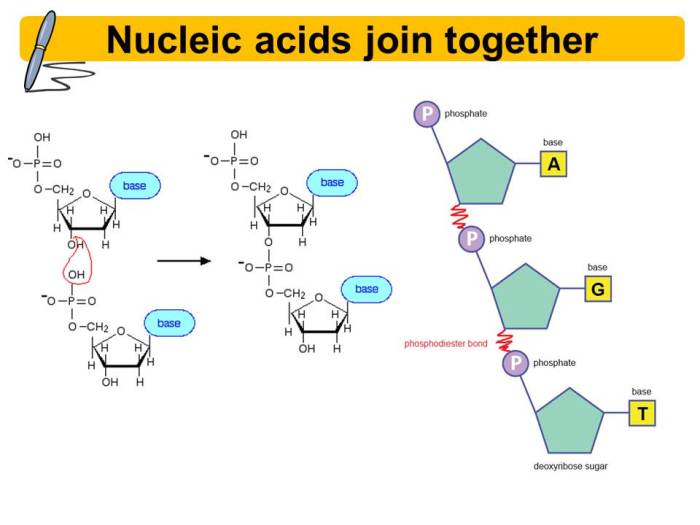
Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, which are linked together by phosphodiester bonds. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA stores genetic information, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis. The structure of nucleic acids is essential for their function, and changes in structure can lead to changes in function.
Biological Molecules and Metabolism
Biological molecules are essential for metabolism, the chemical reactions that occur in cells. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids are interconverted and utilized for energy production and cellular processes. For example, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used as fuel for cellular respiration.
Proteins can be broken down into amino acids, which can be used for energy or to build new proteins. Lipids can be broken down into fatty acids, which can be used for energy or to build new lipids. Nucleic acids are involved in the synthesis of proteins, which are essential for a wide range of cellular processes.
FAQ Resource
What are the four main types of biological molecules?
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Energy source and structural support
What is the role of proteins in biological processes?
Enzymes, hormones, structural components, and more
What is the genetic material composed of?
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)