In the realm of chemistry, ionic and covalent bonds play pivotal roles in shaping the properties of matter. The ionic and covalent bonds venn diagram emerges as a valuable tool, providing a comprehensive visual representation of their contrasting characteristics. This article delves into the intricacies of these two fundamental bond types, exploring their similarities, differences, and practical applications.
Ionic bonds, characterized by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, stand in contrast to covalent bonds, which involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. This introductory paragraph sets the stage for an in-depth analysis of these two distinct bonding mechanisms.
Ionic and Covalent Bonds Venn Diagram
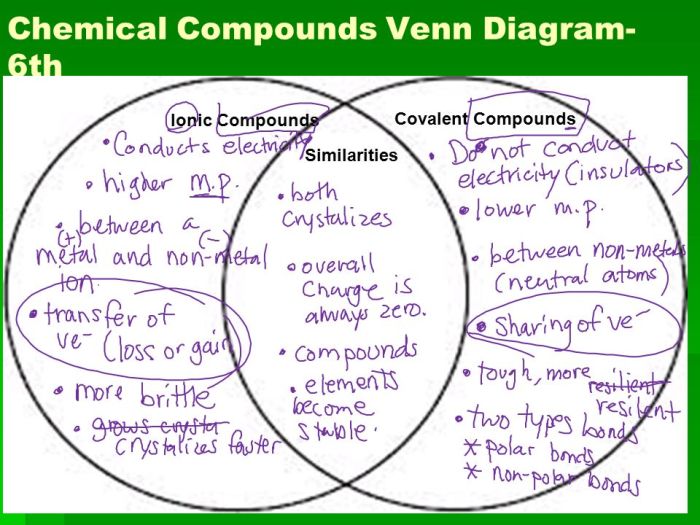
Ionic and covalent bonds are two fundamental types of chemical bonds that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. They differ in the way electrons are shared or transferred between atoms.
An ionic bond is formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, creating positively and negatively charged ions. These ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic compound. A covalent bond, on the other hand, is formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, creating a covalent molecule.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the similarities and differences between ionic and covalent bonds:

As shown in the diagram, ionic and covalent bonds both involve the sharing or transfer of electrons. However, ionic bonds are formed between atoms with a large difference in electronegativity, resulting in the complete transfer of electrons and the formation of ions.
Covalent bonds, on the other hand, are formed between atoms with similar electronegativity, resulting in the sharing of electrons.
Characteristics of Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are characterized by the following properties:
- Formed between atoms with a large difference in electronegativity (typically between a metal and a non-metal).
- Involve the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another, creating positively and negatively charged ions.
- Electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds the compound together.
- Form crystalline solids with a regular arrangement of ions.
- Typically have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces.
- Are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted.
Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium oxide (CaO).
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds: Ionic And Covalent Bonds Venn Diagram

Covalent bonds are characterized by the following properties:
- Formed between atoms with similar electronegativity (typically between non-metals).
- Involve the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between the atoms.
- The shared electrons form a molecular orbital that holds the atoms together.
- Form molecules with a specific molecular structure.
- Typically have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds.
- Are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Examples of covalent compounds include methane (CH 4), water (H 2O), and carbon dioxide (CO 2).
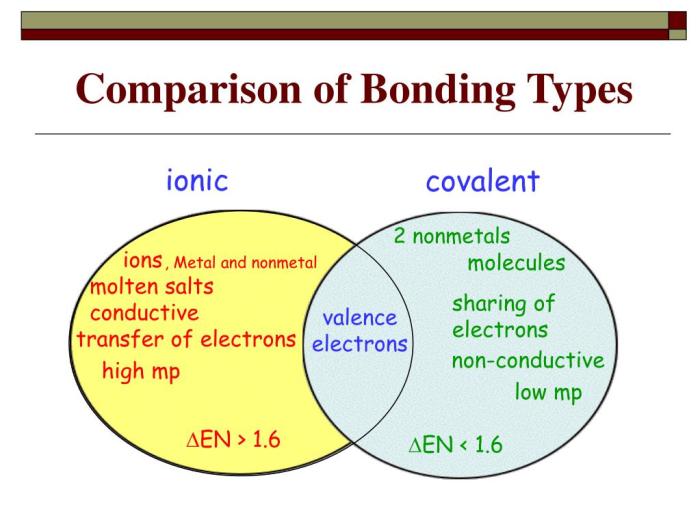
Comparison of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Ionic and covalent bonds differ in the following properties:
| Property | Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Electronegativity difference | Large | Small |
| Electron transfer/sharing | Complete transfer | Sharing |
| Bond strength | Strong | Weaker |
| Polarity | Polar | Nonpolar or polar |
| Solubility | Soluble in water | Insoluble in water |
| Conductivity | Good conductors | Poor conductors |
The type of bond formed between atoms depends on the electronegativity difference between them. If the difference is large, an ionic bond is formed. If the difference is small, a covalent bond is formed.
Applications of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Ionic and covalent bonds are essential for the formation and properties of various materials and compounds. Here are a few examples:
- Ionic bondsare found in table salt (NaCl), which is used for seasoning food and preserving meats. They are also found in concrete, which is used for construction.
- Covalent bondsare found in water (H 2O), which is essential for life. They are also found in plastics, which are used for a wide variety of products, including food packaging, toys, and clothing.
The understanding of ionic and covalent bonds is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and biology.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the key difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of ions, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
How does the ionic and covalent bonds venn diagram help in understanding these bonds?
The venn diagram visually represents the similarities and differences between ionic and covalent bonds, making it easier to compare and contrast their properties.
What are some examples of ionic and covalent compounds?
Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium iodide (KI), while examples of covalent compounds include methane (CH4) and water (H2O).


