Embark on a geometric expedition with Polygons and Quadrilaterals Unit Test Part 1, where we delve into the fascinating world of polygons, unraveling their properties, classifications, and practical applications. This comprehensive test assesses your understanding of these geometric shapes, equipping you with a solid foundation for further exploration in geometry and beyond.
As we navigate through this unit test, we will encounter a diverse array of polygons, including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons, examining their unique characteristics and the criteria used to classify them. We will then focus on quadrilaterals, exploring their distinct features, types, and properties, such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites.
Polygon Identification and Classification: Polygons And Quadrilaterals Unit Test Part 1
Polygons are closed, two-dimensional figures with straight sides. They are classified based on the number of sides they have.
Types of Polygons
- Triangle: A polygon with three sides.
- Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides.
- Pentagon: A polygon with five sides.
- Hexagon: A polygon with six sides.
Criteria for Classifying Polygons
Polygons can be classified based on the following criteria:
- Number of sides
- Number of angles
- Shape of the sides
- Whether the sides are parallel
Quadrilateral Properties and Types
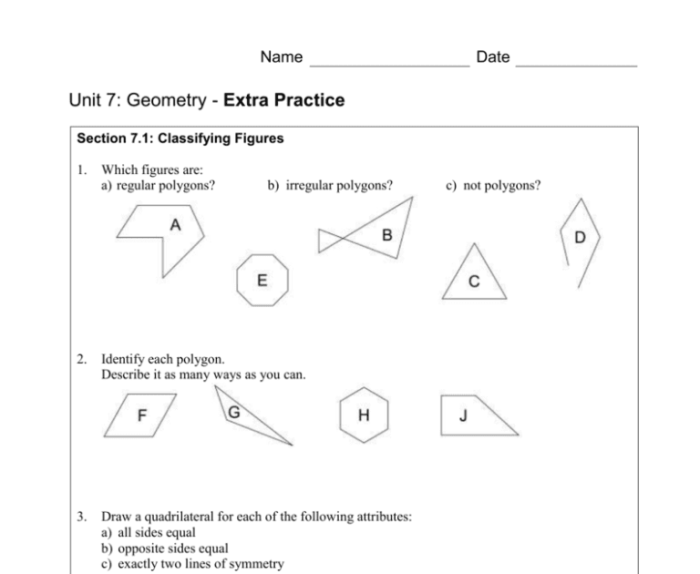
Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. They have unique properties that distinguish them from other polygons.
Types of Quadrilaterals
- Square: A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with four right angles and opposite sides parallel.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel.
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.
- Kite: A quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides equal in length.
Properties of Quadrilaterals
Each type of quadrilateral has its own unique properties, such as:
- Equal sides
- Parallel sides
- Right angles
- Diagonals
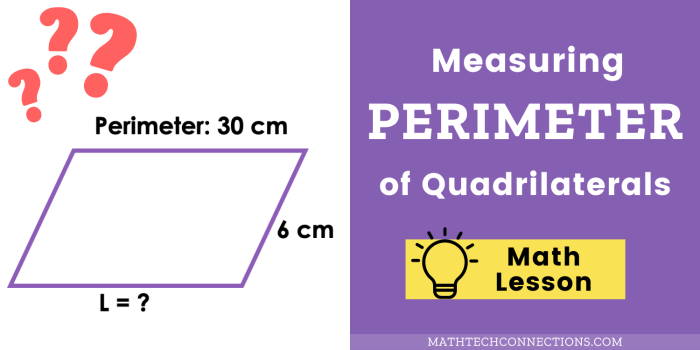
Perimeter and Area of Quadrilaterals
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. The area of a quadrilateral is the amount of space it encloses.
Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
The formula for calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral is:
P = a + b + c + d
where a, b, c, and d are the lengths of the four sides.
Area of a Quadrilateral, Polygons and quadrilaterals unit test part 1
The formula for calculating the area of a quadrilateral depends on the type of quadrilateral. For example, the area of a rectangle is:
A = l × w
where l is the length and w is the width.
Applications of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in a wide variety of real-world applications, including:
Architecture
- Polygons are used to create the shapes of buildings, windows, and doors.
- Quadrilaterals are used to create the shapes of rooms, floors, and roofs.
Engineering
- Polygons are used to design bridges, tunnels, and other structures.
- Quadrilaterals are used to design machines, vehicles, and other equipment.
Design
- Polygons are used to create logos, symbols, and other graphic designs.
- Quadrilaterals are used to create textiles, furniture, and other decorative items.
Top FAQs
What is the difference between a polygon and a quadrilateral?
A polygon is any closed figure with three or more straight sides, while a quadrilateral is a specific type of polygon with four sides.
How do you classify polygons?
Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they have, such as triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), and so on.
What are the different types of quadrilaterals?
There are five main types of quadrilaterals: squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites.