What the investigator varies in the experiment – In scientific experimentation, researchers meticulously manipulate independent variables to observe their effects on dependent variables. This intricate relationship between variables forms the cornerstone of experimental design, allowing scientists to unravel cause-and-effect relationships and gain insights into complex phenomena.
The concept of independent variables, which are deliberately altered by the investigator, is fundamental to the scientific method. By varying these variables, researchers can isolate their specific effects on the dependent variables, which are the outcomes being measured. Understanding this interplay is crucial for drawing valid conclusions and advancing scientific knowledge.
Independent Variables
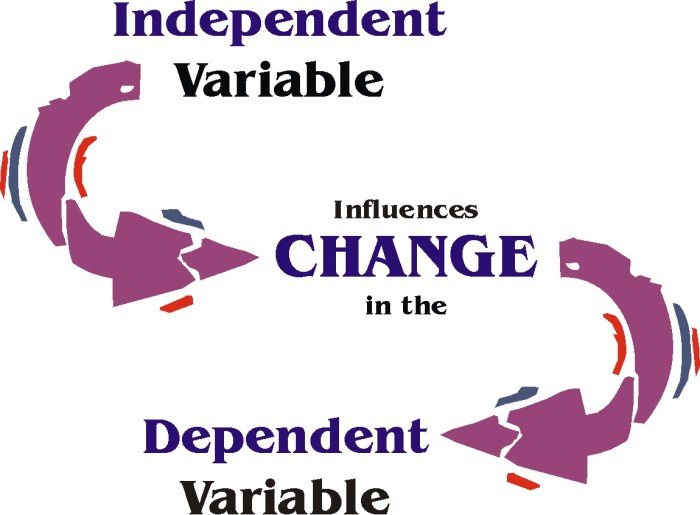
Independent variables are the variables that are manipulated by the investigator in an experiment. They are the variables that are changed or controlled in order to see how they affect the dependent variables.
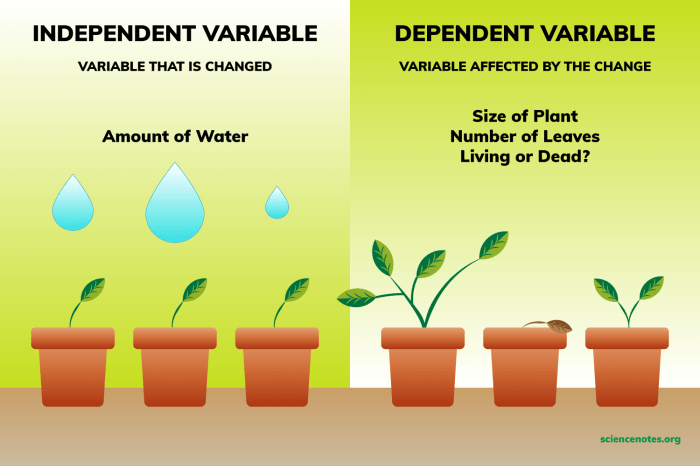
For example, in an experiment to investigate the effects of temperature on the growth of plants, the independent variable would be the temperature. The investigator would change the temperature of the plants and see how it affected their growth.
The purpose of varying independent variables in an experiment is to determine how they affect the dependent variables. By changing the independent variables, the investigator can see how the dependent variables change in response.
Dependent Variables
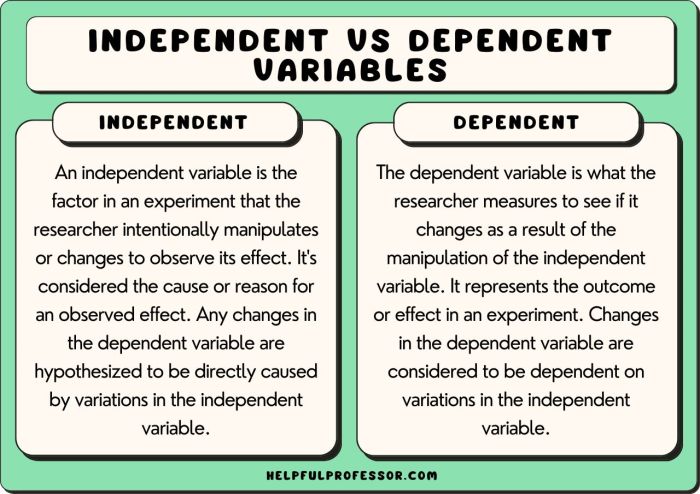
Dependent variables are the variables that are measured in an experiment. They are the variables that are affected by the independent variables.
For example, in an experiment to investigate the effects of temperature on the growth of plants, the dependent variable would be the growth of the plants. The investigator would measure the growth of the plants and see how it changed in response to the different temperatures.
Dependent variables are often quantified using a variety of methods, such as measuring, counting, or weighing. The method of quantification will depend on the nature of the dependent variable.
Controlled Variables: What The Investigator Varies In The Experiment
Controlled variables are the variables that are kept constant in an experiment. They are the variables that are not changed or manipulated by the investigator.
For example, in an experiment to investigate the effects of temperature on the growth of plants, the controlled variables might include the type of plant, the amount of water given to the plants, and the amount of light the plants receive.
The purpose of controlling variables in an experiment is to ensure that the only variable that is changing is the independent variable. This allows the investigator to isolate the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
Experimental Design
Experimental design is the process of planning and conducting an experiment. The goal of experimental design is to create an experiment that will provide valid and reliable results.
There are many different experimental designs that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common experimental designs include:
- True experimental design:This is the most rigorous type of experimental design, and it involves randomly assigning participants to different treatment groups.
- Quasi-experimental design:This type of experimental design is less rigorous than a true experimental design, but it can still be used to investigate causal relationships.
- Non-experimental design:This type of experimental design does not involve randomly assigning participants to different treatment groups. Instead, the researcher simply observes the relationship between variables.
The choice of experimental design will depend on the research question being investigated and the resources available.
Data Analysis

Data analysis is the process of analyzing the data collected in an experiment. The goal of data analysis is to determine whether the results of the experiment support the hypothesis.
There are many different statistical tests that can be used to analyze data, each with its own assumptions and requirements. The choice of statistical test will depend on the type of data collected and the research question being investigated.
It is important to note that data analysis is not simply a matter of running a statistical test and reporting the results. The researcher must also interpret the results of the statistical test and draw conclusions about the relationship between the variables.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of varying independent variables in an experiment?
Varying independent variables allows researchers to isolate their specific effects on dependent variables, enabling them to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
How are dependent variables measured?
Dependent variables are measured using appropriate measurement tools or techniques that quantify the observed changes or outcomes.
Why is it important to control variables in an experiment?
Controlling variables eliminates or minimizes the influence of extraneous factors, ensuring that the observed effects are solely due to the manipulation of independent variables.