Match each event with the appropriate stage of meiosis – Understanding meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes, is crucial for comprehending genetic inheritance and diversity. This guide provides a detailed exploration of meiosis, meticulously matching key events with their corresponding stages, offering a comprehensive overview of this fundamental biological process.
Introduction
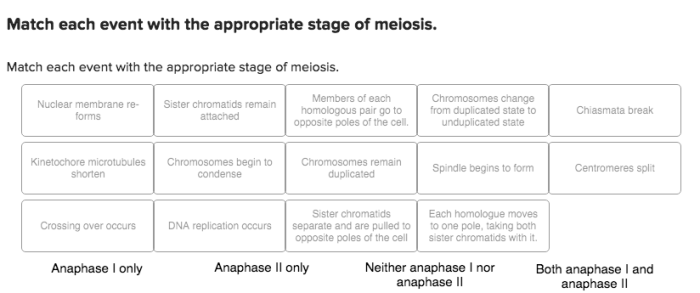
Meiosis is a specialized cell division that produces gametes (eggs and sperm) in sexually reproducing organisms. It involves two rounds of division, known as meiosis I and meiosis II, resulting in four haploid daughter cells. Understanding meiosis is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of genetic inheritance, variation, and the maintenance of species diversity.
Matching Events to Meiosis Stages
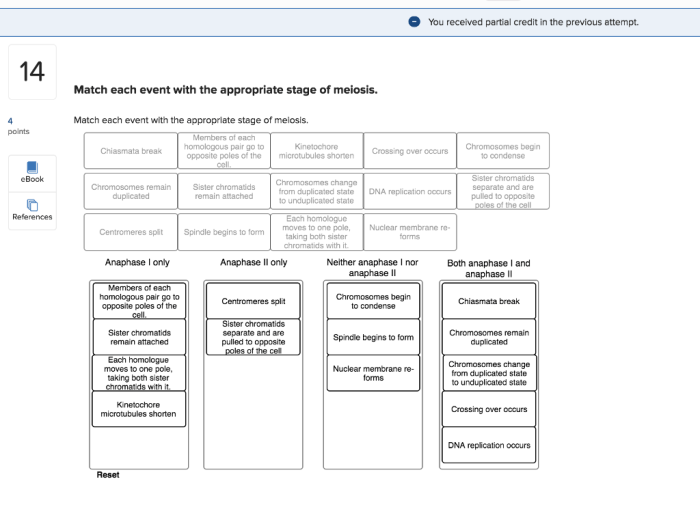
| Event | Stage of Meiosis |
|---|---|
| Homologous chromosomes pair up | Prophase I |
| Chromosomes line up at the equator | Metaphase I |
| Chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles | Anaphase I |
| Cytokinesis occurs, producing two haploid daughter cells | Telophase I |
| Chromosomes line up at the equator again | Metaphase II |
| Chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles again | Anaphase II |
| Cytokinesis occurs, producing four haploid daughter cells | Telophase II |
Elaborate on Meiosis Stages: Match Each Event With The Appropriate Stage Of Meiosis
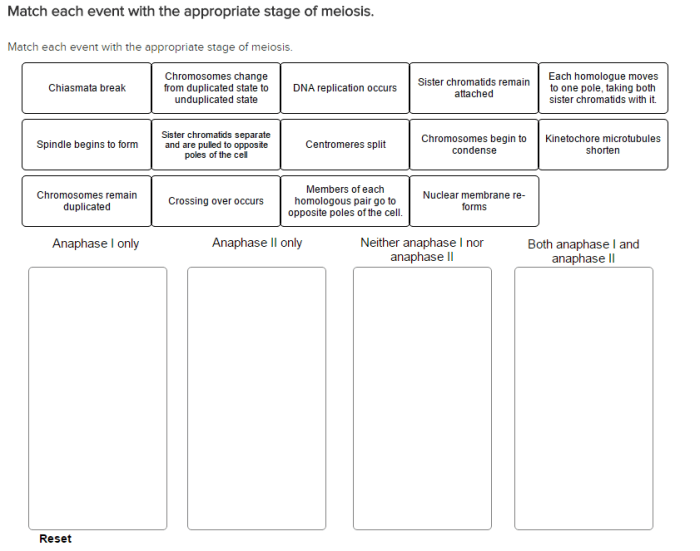
Prophase I
Prophase I adalah tahap terpanjang dan paling kompleks dalam meiosis. Ini ditandai dengan:
- Replikasi kromosom
- Pembentukan tetrad (pasangan kromosom homolog yang terikat)
- Pertukaran materi genetik melalui crossing-over
Metaphase I
Pada metafase I, tetrad berjajar di sepanjang bidang ekuator sel. Spindel serat menempel pada kromosom dan bersiap untuk memisahkannya.
Anaphase I, Match each event with the appropriate stage of meiosis
Selama anafase I, kromosom homolog memisahkan dan bergerak ke kutub sel yang berlawanan. Ini menghasilkan dua sel haploid, masing-masing berisi satu set kromosom yang belum direplikasi.
Telophase I
Pada telofase I, kromosom mencapai kutub sel dan dekonversi menjadi kromatin. Sitokinesis terjadi, menghasilkan dua sel haploid yang terpisah.
Meiosis II
Meiosis II mirip dengan mitosis, dengan dua perbedaan utama:
- Sel-sel yang memasuki meiosis II sudah haploid.
- Tidak ada replikasi kromosom sebelum meiosis II.
Applications and Implications
Meiosis memiliki aplikasi yang luas dalam genetika dan biologi:
- Genetika:Meiosis menjelaskan bagaimana sifat diturunkan dari orang tua ke keturunannya, menciptakan variasi genetik yang mendorong evolusi.
- Reproduksi:Meiosis menghasilkan gamet haploid yang diperlukan untuk fertilisasi dan reproduksi seksual.
- Kesehatan manusia:Meiosis dapat menyebabkan kelainan genetik jika terjadi kesalahan selama proses. Memahami meiosis sangat penting untuk diagnosis dan pengobatan kelainan ini.
Query Resolution
What is the significance of meiosis?
Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction, producing gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It promotes genetic diversity through recombination, contributing to the evolution and adaptation of species.
How many stages are there in meiosis?
Meiosis consists of two divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, each with prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase stages.
What is the key difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse gametes. Meiosis involves chromosome pairing and recombination, leading to genetic variation.