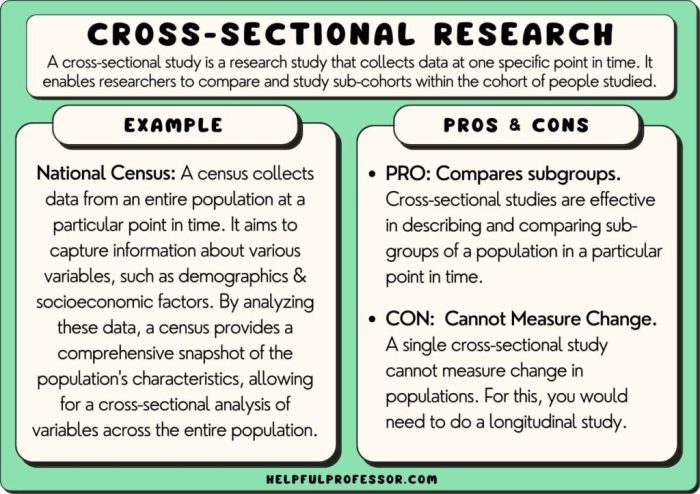
Which of the following is true of cross-sectional research? Cross-sectional research is a type of observational study that collects data from a sample of the population at one point in time. This type of research is often used to describe the characteristics of a population or to compare different groups of people.
Cross-sectional studies are relatively easy to conduct and can provide valuable information about a population. However, they also have some limitations. One limitation is that cross-sectional studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships. Another limitation is that the results of cross-sectional studies can be affected by sampling error.
Understanding Cross-Sectional Research
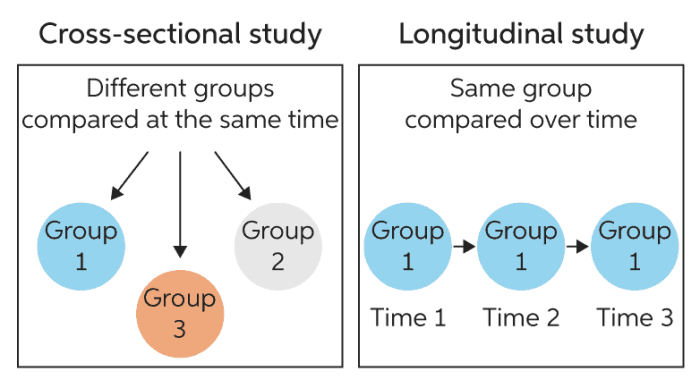
Cross-sectional research is a research design that involves collecting data from a sample of individuals at a single point in time. It aims to provide a snapshot of the characteristics, opinions, or behaviors of a population at a specific moment.Cross-sectional
studies are often used to explore relationships between variables, identify trends, and make comparisons between different groups. For example, a cross-sectional study could be used to investigate the relationship between age and health status, or to compare the voting preferences of different demographic groups.
Key Characteristics of Cross-Sectional Research, Which of the following is true of cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional research has several distinguishing features compared to other research designs:
- Observational: Cross-sectional studies observe participants without manipulating or intervening in the variables of interest.
- Single Time Point: Data is collected at a single point in time, providing a snapshot of the population.
- Non-Longitudinal: Cross-sectional studies do not follow participants over time, making it difficult to establish causal relationships.
- Descriptive: Cross-sectional research typically provides a description of the population at a specific point in time, rather than making predictions or inferences about future outcomes.
Advantages of Cross-Sectional Research
- Cost-effective and efficient: Cross-sectional studies are relatively inexpensive and can be conducted quickly.
- Provides a snapshot of the population: Cross-sectional studies can provide a valuable snapshot of the characteristics, opinions, or behaviors of a population at a specific point in time.
- Useful for exploring relationships and trends: Cross-sectional studies can help researchers identify relationships between variables and explore trends over time.
Disadvantages of Cross-Sectional Research
- Difficult to establish causality: Cross-sectional studies cannot establish causal relationships between variables due to their non-longitudinal nature.
- Limited generalizability: The results of cross-sectional studies may not be generalizable to other populations or time periods.
- Subject to bias: Cross-sectional studies are susceptible to selection bias, non-response bias, and measurement bias.
Detailed FAQs: Which Of The Following Is True Of Cross-sectional Research
What is cross-sectional research?
Cross-sectional research is a type of observational study that collects data from a sample of the population at one point in time.
What are the advantages of cross-sectional research?
Cross-sectional studies are relatively easy to conduct and can provide valuable information about a population.
What are the limitations of cross-sectional research?
Cross-sectional studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships and the results can be affected by sampling error.