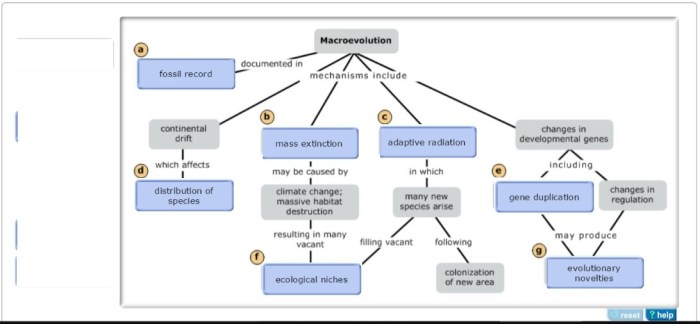
Evolution concept map answers key provides an indispensable guide to understanding the fundamental principles that govern the evolution of life on Earth. This comprehensive resource unravels the intricate mechanisms and compelling evidence that support the theory of evolution, offering a profound insight into the dynamic nature of our planet’s biodiversity.
Through a meticulous examination of key concepts, historical developments, and scientific advancements, this concept map unveils the remarkable journey of evolutionary thought, illuminating the contributions of pioneering scientists and the transformative impact of their discoveries.
1. Key Concepts: Evolution Concept Map Answers Key
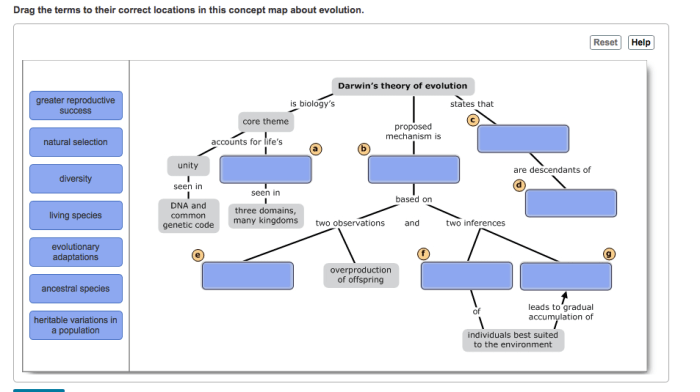
Evolution is the process by which the genetic composition of a population changes over generations. The theory of evolution by natural selection, proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, explains how organisms with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous genes to future generations.
This leads to the gradual accumulation of favorable traits in a population, resulting in adaptation to their environment and the evolution of new species.
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the driving force behind evolution. It occurs when individuals with certain heritable traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing in their environment. These traits, which can range from physical characteristics to behavioral adaptations, provide a selective advantage to their possessors.
Over time, the frequency of these advantageous traits increases in the population, leading to evolutionary change.
Adaptation
Adaptation refers to the traits or characteristics of an organism that enhance its survival and reproductive success in a specific environment. Adaptations can be structural, physiological, or behavioral. For example, the thick fur of arctic animals helps them survive in cold climates, while the camouflage of insects helps them avoid predators.
Speciation
Speciation is the process by which new species arise from existing ones. It can occur through various mechanisms, such as geographic isolation, genetic drift, or natural selection. When populations of a species become reproductively isolated, they can diverge genetically and eventually become distinct species.
2. Mechanisms of Evolution
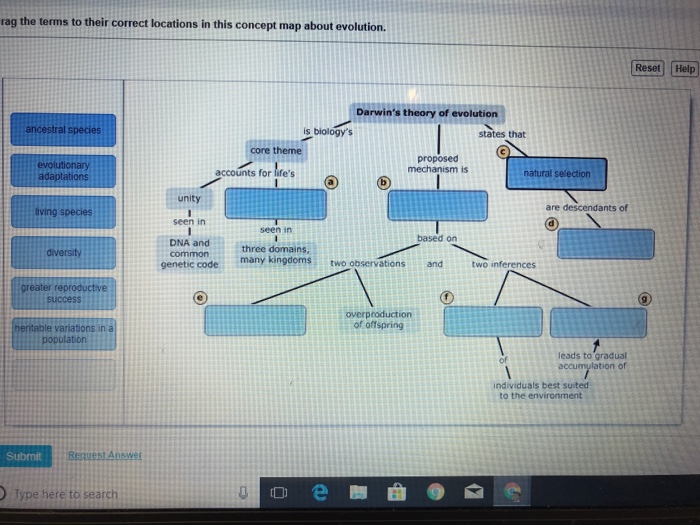
Evolution occurs through various mechanisms that contribute to genetic variation and the differential survival and reproduction of individuals. These mechanisms include genetic variation, mutation, gene flow, genetic drift, and non-random mating.
Genetic Variation, Evolution concept map answers key
Genetic variation is the presence of differences in the genetic makeup of individuals within a population. It arises from various sources, including mutations, genetic recombination, and gene flow. Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
Mutation
Mutation is a random change in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be caused by environmental factors, such as radiation or chemicals, or they can occur spontaneously during DNA replication. While most mutations are harmful, some can be beneficial, providing new genetic variation for natural selection to act upon.
Gene Flow
Gene flow is the movement of genes between populations. It can occur through migration, interbreeding, or the introduction of new individuals into a population. Gene flow can introduce new genetic variation into a population and influence the frequency of alleles.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is the random change in allele frequencies in a population. It can occur due to chance events, such as the loss of individuals during a population bottleneck. Genetic drift can lead to the loss of genetic variation and the fixation of certain alleles in a population.
Non-Random Mating
Non-random mating refers to the preferential mating of individuals with certain traits. This can occur due to factors such as mate choice, assortative mating, or sexual selection. Non-random mating can influence the frequency of alleles in a population and contribute to the evolution of specific traits.
Detailed FAQs
What is the central concept of evolution?
The central concept of evolution is natural selection, which describes the process by which organisms with traits that make them better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring.
What are some examples of evidence for evolution?
Evidence for evolution includes fossils, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, and the observation of evolutionary changes in living populations.
What are some common misconceptions about evolution?
Common misconceptions about evolution include the idea that evolution is a linear progression, that humans are descended from apes, and that evolution is a random process.
What are some practical applications of evolutionary theory?
Practical applications of evolutionary theory include the development of new medical treatments, the improvement of agricultural practices, and the conservation of endangered species.