IV therapy and peripheral access pretest play a pivotal role in healthcare settings, enabling the safe and effective administration of fluids and medications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of IV therapy, peripheral access techniques, and the importance of pretests to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
The subsequent paragraphs provide detailed insights into the various aspects of IV therapy and peripheral access, offering a comprehensive understanding of this essential aspect of healthcare practice.
1. Definition and Importance of IV Therapy: Iv Therapy And Peripheral Access Pretest

Intravenous (IV) therapy involves the administration of fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into a vein through a small tube called an IV catheter. It is a critical intervention in healthcare settings, providing a direct and controlled route for delivering essential substances to patients.
IV therapy is essential for various medical conditions, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, blood loss, and the administration of antibiotics, chemotherapy, and other medications. Common IV fluids include normal saline, lactated Ringer’s, and dextrose solutions, while common medications administered via IV include antibiotics, pain relievers, and fluids for resuscitation.
2. Peripheral Access Techniques
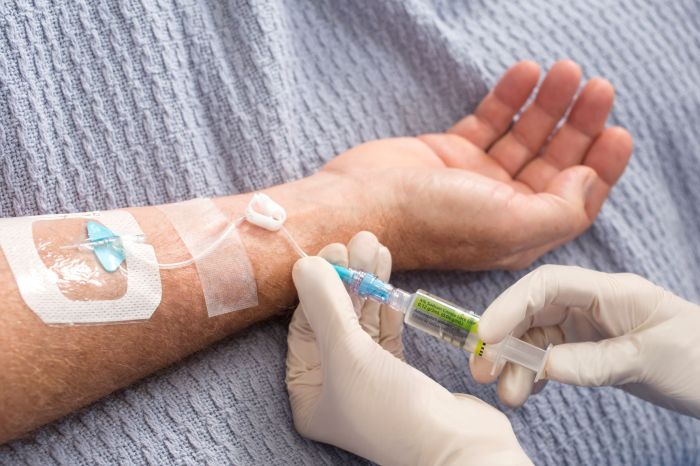
Venipuncture
Venipuncture is the most common peripheral access technique, involving the insertion of a needle into a vein to obtain blood or administer fluids or medications. It is typically performed on the veins in the antecubital fossa (inner elbow) or the back of the hand.
Advantages:Easy to perform, relatively painless, and allows for quick access to veins.
Disadvantages:Can be challenging in patients with small or difficult-to-access veins, and repeated punctures can cause discomfort.
Peripheral IV Catheter Insertion, Iv therapy and peripheral access pretest
Peripheral IV catheter insertion involves placing a small, flexible catheter into a vein, allowing for longer-term IV access. It is commonly used for patients requiring ongoing IV fluids or medications.
Advantages:Provides reliable and long-term access, reduces the need for multiple venipunctures, and is less painful than venipuncture.
Disadvantages:Can be more time-consuming to insert and requires more training, and the catheter can become dislodged or infected.
Midlines
Midlines are longer IV catheters that are placed in a larger vein in the upper arm. They are used for patients who require IV therapy for an extended period, such as those receiving chemotherapy or antibiotics.
Advantages:Provides reliable and long-term access, reduces the risk of infection, and allows for the administration of vesicant medications.
Disadvantages:More invasive to insert, requires more training, and can be more uncomfortable for patients.
FAQ Summary
What is the purpose of an IV therapy pretest?
An IV therapy pretest helps identify potential risks and contraindications associated with IV therapy, ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes.
What are the different types of peripheral access techniques?
Common peripheral access techniques include venipuncture, peripheral IV catheter insertion, and midlines, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Why is patient education important in IV therapy?
Patient education empowers individuals to understand the purpose, benefits, and potential risks of IV therapy, promoting informed decision-making and adherence to treatment plans.
